-
Digital Marketing
We help you to use your digital potential. For a strong positioning, more visibility and more leads.
Get Growth ready
With the BEE.Transformance model, we bring continuous and profitable growth to your company. A new mindset for your team.
Industries
We transform your challenges into opportunities through the experience we have gained from projects in these industries.
-
HubSpot Services
As a HubSpot Diamond Partner, we help you implement your digital growth strategy with a focus on performance - by implementing and integrating new and existing systems as well as 3rd party apps.
HubSpot Thought Leader
As a HubSpot Diamond Partner with +50 certifications, host of the HubSpot User Group Zurich, HubSpot Trainer and HuSpot User Champions, you have access to in-depth HubSpot expertise.
HubSpot Solutions
The BEE.Theme offers you more creative freedom than any other theme on the market. Whether you're a beginner or a professional, a creative mind or a digital agency - with the BEE theme, you can easily unleash the maximum power for your pages in HubSpot CMS.
-
BEE.Blog
Knowledge around digital marketing, digital sales, technology, data intelligence and employees.
Knowledge Base
Pure knowledge: everything essential concentrated, compact, digitally prepared for you and ready to download.
What is inbound?
The most effective way to successfully combine digital marketing and digital sales.
-
BEE.Team
The BEE.Performers: many different characters - with one thing in common: the fascination for a digital world.
References
More than 100 large and small companies have already started with BEE: to more visibility, more performance, more growth.
Invest
Participate in the growth of BEE and become part of the BEE Growth Story by purchasing Digital Share Tokens.
We're hiring
Become a BEE.Performer! Are you ready for your own transformation?
How to Use Schema Markup to Improve Your Blog Posts
When working hard to produce and publish awesome content, you want to give it every opportunity to reach the intended audience. Visitors to your website should engage with your message and move along the buyer’s journey; otherwise, what’s the point?
Using SEO best practices to rank well on popular search engines should always be part of your strategy, and knowing how to use the common language between search engine crawlers and webpages is part of that strategy.
Schema markup is the name typically used when talking about the language that helps search engines recognise and make sense of your content — a process where the search engine’s crawlers look at the textual and visual elements you’ve implemented.
A good understanding of schema markup will help you to position your content as relevant and useful to the querent. If you do this well, you may even win the featured snippet spot on Google and get a better click-through rate (CTR) for your website.
Since schema markup is basically a code, some may be immediately put off by this more technical side of content creation. But fear not! We’ll explain exactly what schema markup is and how you can start using it to boost your position on the search engine results page (SERP).
What is schema markup?
Another name for schema markup is structured data. It’s the language that search engines use to read and understand the content on your web pages. This language uses code (semantic vocabulary) that will help the search engine categorise the content on each page.
Unlike humans, a search engine doesn’t share your visual abilities or intuition, so it can’t make the kind of assumptions that you may be able to when trying to ascertain whether a piece of content hits the spot in answering your question. It needs help to identify, read and assign meaning to the content, and that’s where schema markup comes in.
Below, we show you what things look like through the human lens and the search engine’s goggles:
What you see:
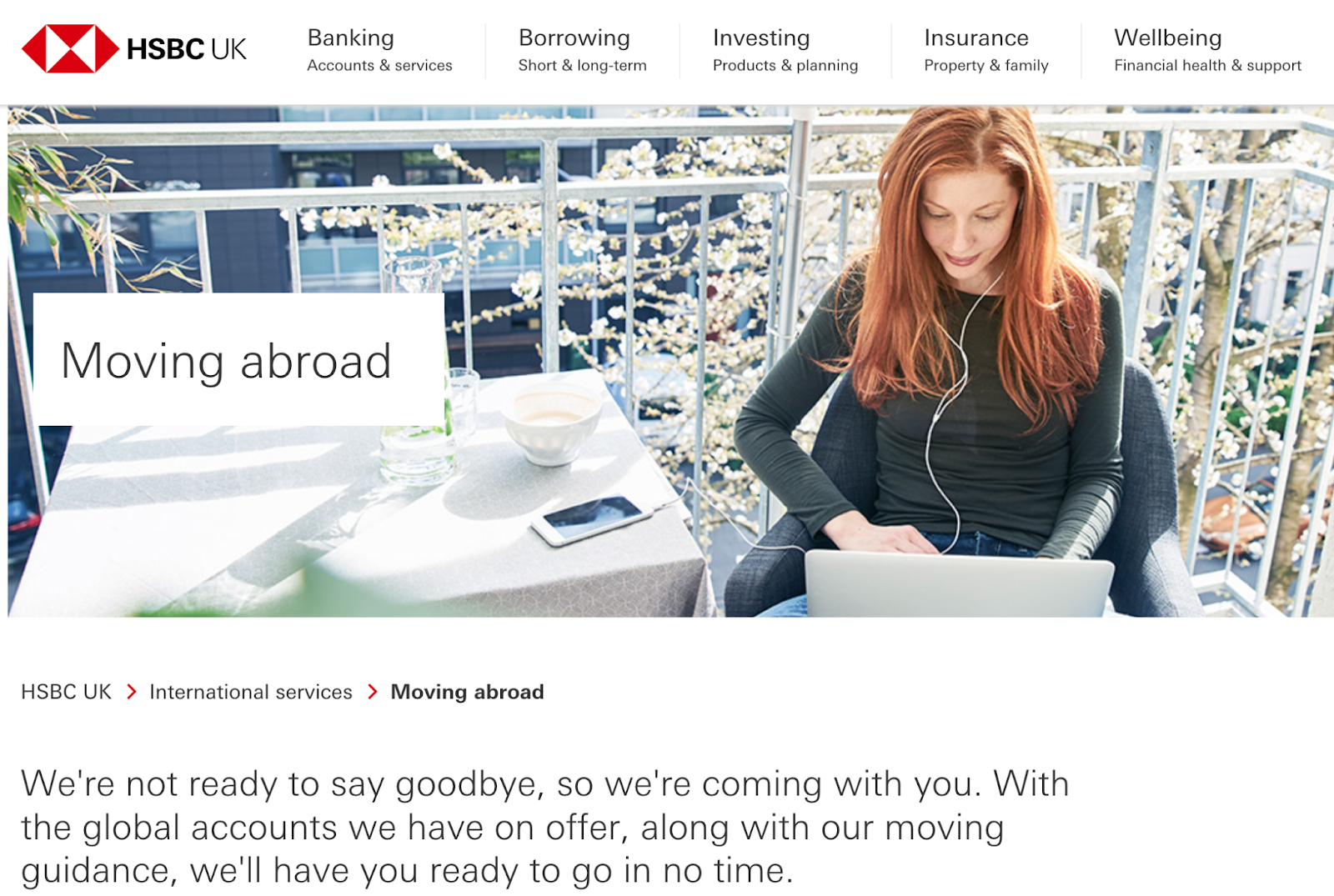
What a search engine sees:
Structured data is basically standardised web page information in code format that tells the search engine what the meaning of the content on the page is — an invisible translator, if you like.
A short definition of schema markup: The semantic vocabulary a search engine uses to understand and classify content on a web page.
Why is schema markup important?
Imagine it’s your job to sift through thousands of documents every day. You have to make sense of everything you see and organise the documents by category. Then, you have to rank them for multiple factors and ensure that they fit certain criteria so that you can deliver those documents to the right people. You’d appreciate it when someone makes your day a little easier, right?
Search engines like websites that use structured data because it’s quicker to understand the meaning of each page and helps them present high-quality results to their users.
Webmasters using schema markup can help create a better a user experience for querents because the search engine can extract other useful nuggets such as reviews or offers, enabling the person conducting the search to make a decision faster as to whether they should click on your link and find out more. This type of rich data is a fantastic way to boost your content’s visibility and attract visitors to your website. Schema markup also makes your pages easier to index, further supporting your SEO strategy.
How to use schema markup
Schema.org is a website created by Bing, Google and Yahoo; there, you will find over 760 different types of schemas listed. The website serves as a guide for the common set of schemas for structured data. If you’re worried about which one of these hundreds of schemas to implement, don’t worry, Google’s done a good job of breaking down the specific schemas that will help your blogs show up as rich results – explore Google’s search gallery documentation here.
JSON-LD is the data format you’re most likely to come across and use — it’s easy to read and human-friendly. For example, if you had a recipe page and you wanted the featured snippet to describe the recipe title, author, and any additional details, this is what the JSON-LD structured data may look like:

Schema markup has many use cases; you can choose to include microdata that helps you highlight certain points of interest about your product or service, such as:
- Pricing
- Reviews
- Opening hours
- Location
- Reviews
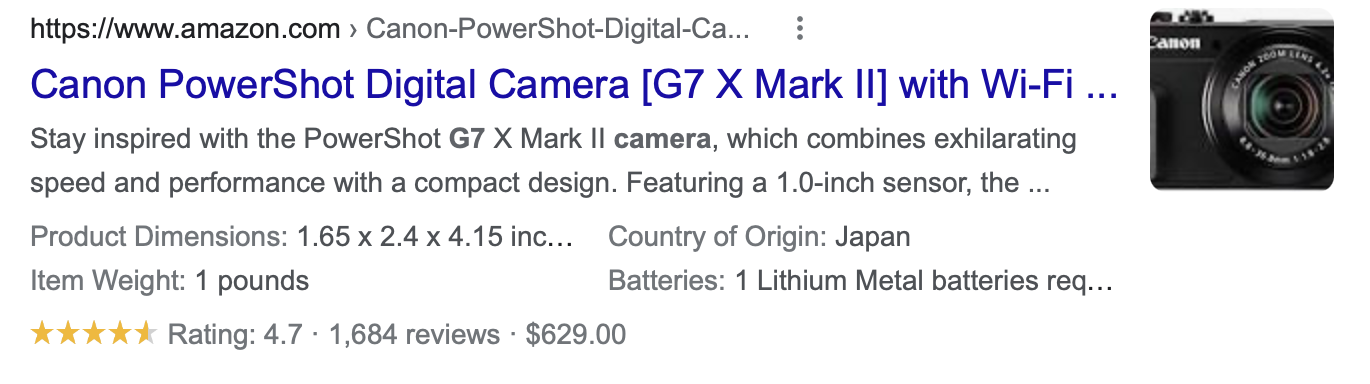
This method of enhancing your search engine listing helps potential customers to get their key questions answered quickly. For example, if you were looking for a good vlogging camera within a specific budget, it’s much easier to conduct your research when the reviews and pricing show up on the SERP without you having to click on the link first.
Using schema markup in HubSpot
Enhancing your blogs in HubSpot can be pretty straightforward. You can choose a template or module implementation based on the situation.
Adding code to a template
If you regularly publish a news article, you’re likely using a consistent single schema. This means you only need to build an article schema at the template level of your content, and whoever is uploading and publishing your content doesn’t have to do any additional work.
Creating a custom module
Say you need multiple schema types because you publish articles, events, and new career opportunities; you can create options that the content editor can select when each piece of content is ready to be published.
If you’re unfamiliar with the code, you can acquire the services of a developer or use the Schema Markup integration that automates this task for you.
Alternatively, there’s the Google Structured Data Markup Helper, here’s how:
Step 1: Open up helper.
Step 2: Choose the type of listing to which you want to add structured data, then paste the URL in the form field.
Step 3: Type in the information you want to show up.
Step 4: Click the “Create HTML” button.
Step 5: Select the yellow, highlighted code ( your markup code) and copy and paste it — or hit “download”.
Step 6: Place the code in your CMS.
Lastly, be sure to test that the schema markup shows up as you intend; you can do this by using the Google Structured Data Testing Tool.
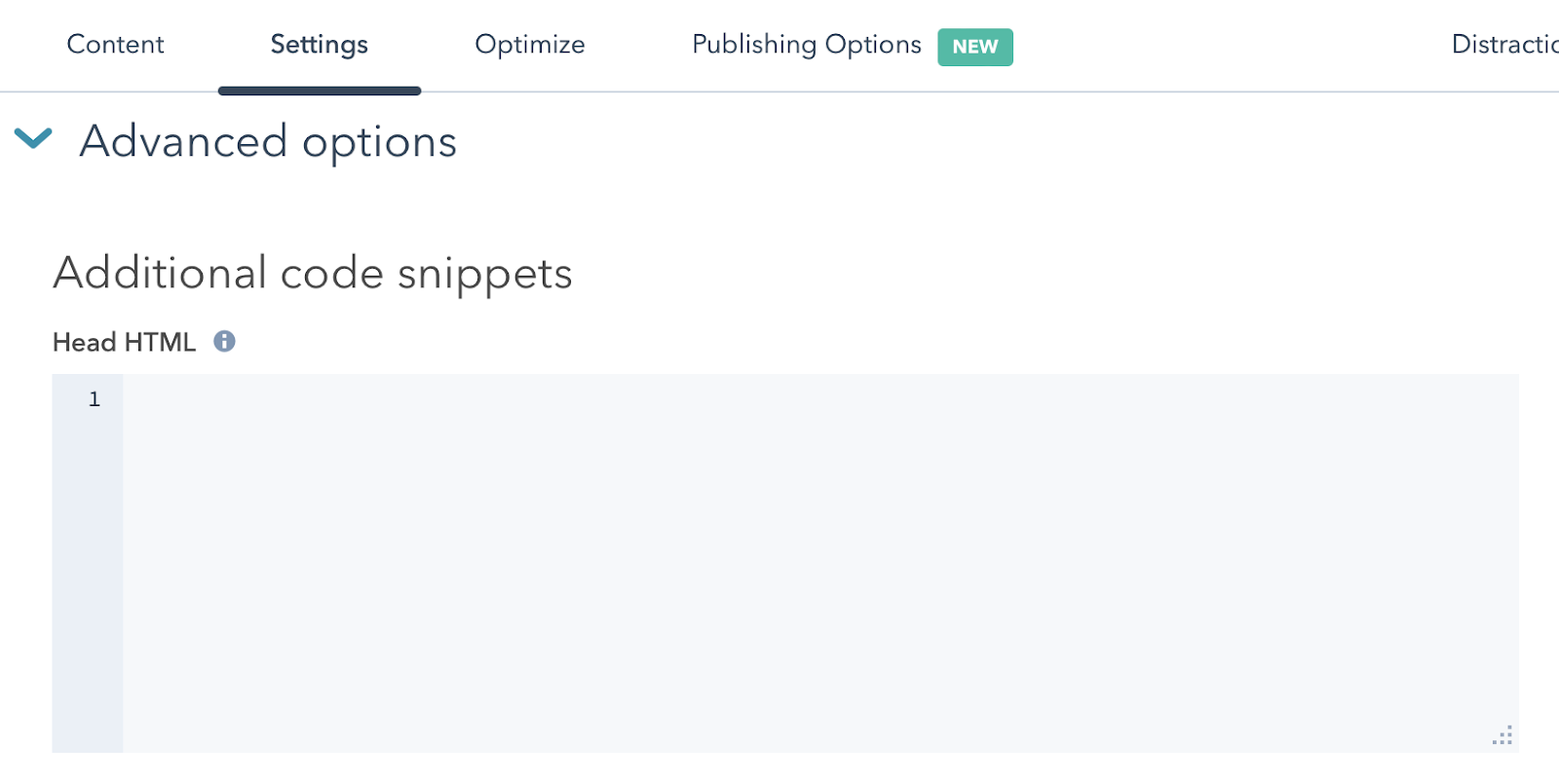
When we’re talking specifically about individual blogs in HubSpot, you can now add custom HTML into the head section of each blog. It’s where you’d add custom scripts so that you have more control over how your blog is presented in search results. Here’s what you need to do:
- Go to a blog in your HubSpot editor
- Click the Settings tabClick
- Advanced Options
- Add your customer HTML into the Head HTML field.
Conclusion
If, after reading this article, you feel inspired to make your blogs super search engine-friendly by using schema markup, we can help ensure that you understand the best practices and applications well.
By reviewing your existing SEO strategy as well as the tools and methods you are using to upload and publish content, we can help you achieve more growth and attract better-qualified traffic. Apply for our free SEO check and talk to an expert at BEE Digital about how our services can be tailored to your needs.
Related Posts

Customer Reactivation: Why this strategy is so beneficial
Manuela Krapf | 26 Jan 2023
Acquiring new customers can be a costly endeavour for businesses, but losing them is even more expensive. That's why you should really view your existing customers as an ...
reading time: 9min
Zum Blog
5 Marketing Objectives for 2024
Manuela Krapf | 22 Dec 2023
As the new year unfolds, the marketing landscape welcomes fresh upgrades to processes, novel opportunities, and, most importantly, a chance to reassess marketing ...
reading time: 5min
Zum Blog
HubSpot Reporting: Best Practices and Things You Must Know
Yvette Veigel | 15 Sep 2022
Sales and marketing reports are powerful tools you can rely on when making essential business decisions and planning for the future. Each campaign you launch opens the ...
reading time: 10min
Zum Blog
